How AI Is Reshaping Data Center Segmentation and Operations

What exactly is a data center, and how does it operate? What are the many sorts of data centers, and what function do they play in the organizations that use them?
These appear to be basic questions, yet finding satisfactory solutions may be surprisingly challenging. This post will give you a better understanding of the evolution of AI data center growth and AI data center requirements.
AI is Redefining Data Center Segmentation: Traditional Models Fall Short

For years, we have distinguished between two main areas of the data center demand growth. On the one hand, general-purpose colocation data centers handle workloads businesses no longer wish to keep on-premises. On the other hand, high-value, highly linked locations are often found in heavily inhabited regions. These network-dense interconnection points center ecosystems like financial trading, gaming, and others that rely heavily on low-latency connections. Does this segmentation still benefit us when deciding where to co-locate AI in data center workloads?
When businesses explore colocation data centers for “lifting and shifting” current application workloads away from their on-premises data centers, the choice is frequently based on cost and efficiency. Because their primary goal is to achieve the lowest cost per compute cycle, they may be willing to trade off network density for sites with the lowest real estate and electricity expenses.
We’ve long believed that a single-minded priority for cost is damaging to digital businesses. There is value in running certain workloads in specific locations; in many cases, this entails deploying infrastructure near network-dense areas in major population centers. Data centers that provide extensive interconnectivity to partners and end users may be more expensive initially, but the financial benefit they may give much outweighs this.
Looking at data centers as mere commodities can be especially destructive these days, thanks in large part to the rising role of AI. It is an undeniable reality that if you want to conduct AI properly, the location of your infrastructure is critical. The AI model life cycle is based on many workloads, each with its own infrastructure needs. This means that AI infrastructure should be spread, which may require us to reconsider how we look at various aspects of the data center business.
Understanding Data Centers in the Age of Artificial Intelligence
Instead of the typical two-segment method based just on network density, investigate how we may use AI requirements to develop a more comprehensive segmentation strategy. What distinguishes AI data center infrastructure is the high-power density needs of the latest generation of GPU chipsets. Applying power density as a second segmentation dimension results in a simple 2×2 matrix, as seen below. The vertical axis runs from low to high density, and the horizontal axis runs from high to low latency.
Based on the figure below, there are four types of AI in data centers today.
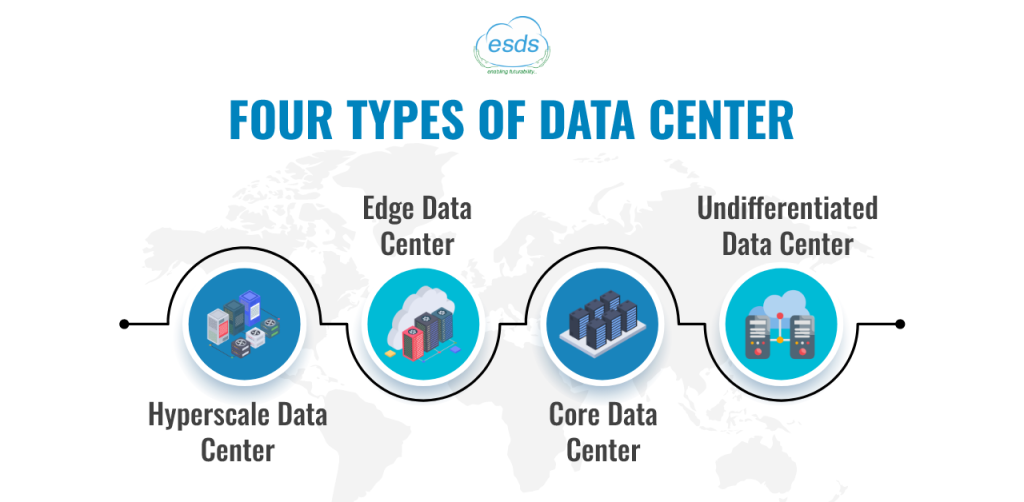
1. Undifferentiated Data Center
A considerable fraction of the world’s data centers are undifferentiated AI data centers. These data centers are generally the result of previous infrastructure investment schemes. Instead of creating data centers in network-dense areas, businesses frequently preferred to put them where most of their personnel lived (such as campuses). Similarly, service providers turned office buildings or warehouses into data centers, transforming previously unsuitable real estate into IT real estate.
While these data centers can provide fit-for-purpose capabilities for a specific set of workloads, what happens when the power density needs of the new workloads skyrocket? How easy is it to update sites for extra liquid cooling and electricity or to implement new cooling technologies like liquid cooling? Enterprises that rely on these undifferentiated data centers for their AI initiatives will most likely fail to implement them successfully.
2. Hyperscale Data Center
When you want extremely high density but are less concerned with low-latency connectivity, hyperscale AI data centers are the ideal solution. These have generally been the purview of big cloud and as-a-service vendors. Instead of needing to construct their own and install new high-density equipment to support their power AI plans, businesses may rent capacity in one of these hyperscale data centers on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Hyperscale data centers have usually been linked with LLM training workloads, which are dense and compute-intensive but less sensitive to latency. However, it would be incorrect to assume that all model training workloads should be routed only through hyperscale data centers. As we’ll see later, there should always be nuance when it comes to choosing the best location for your AI workloads.
3. Edge Data Center
Edge AI data centers, as the name implies, are situated at the digital edge, in close proximity to densely populated end users, applications, and devices. This closeness is critical since many applications and workloads demand consistent low latency.
In edge AI data centers, power data center requirements have not increased at the same rate as other sectors. Edge data centers often run network-heavy workloads that are less density-intensive than compute workloads.
Edge data centers play an important role in AI data centers. Certain AI inference workloads may have extremely low latency requirements. Consider specific gaming use cases or the implementation of digital twins to enable a virtual maintenance assistant. In these instances, organizations may decide to integrate AI inference into their edge data centers. In other circumstances, if latency tolerance is enough, organizations may decide to aggregate their AI inference requirements to their core interconnection hubs, allowing them to administer these models at scale.
4. Core Data Center
Core AI data centers are the core of modern digital infrastructure. They are often located in areas with high network density and closeness, allowing technology consumers and providers to interact and optimize economic value for both sides. Enterprises may build up their internationally dispersed digital infrastructure to provide a comprehensive edge-to-cloud strategy, beginning with linked core data centers. As a result, businesses may improve connections, increase agility, and position themselves to benefit from new technologies like AI.
ESDS, a modern data center services provider, can help future-proof your business
ESDS AI Data Center, in short, fuses cutting-edge AI energy and high-performance computing infrastructure to deliver the most unparalleled efficiencies, scalability, power distribution, and security. ESDS uses next generations data centers, is deeply committed to innovation and sustainability, and becomes the trusted partner of choice when businesses are looking to transform their digital infrastructure to stay ahead in today’s technology-driven, highly competitive landscape and AI data center power demand.
- Why Do You Need Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing? - March 13, 2025
- How to Choose the Right Private Cloud Service Provider in 2025? - February 27, 2025
- Why Cloud Migration is Essential: Benefits, Challenges, and Expert Tips - February 24, 2025
