Advantages of GIS Technology in Core Banking

A Group of networked bank branches providing core banking services to customers. So it provide facility to customers to make transactions and access their funds easily from any member branch bank office. Core banking is nothing but banking institutions conducting business with their retail and small business customers. Most of the banks treating core banking consumers for their retails consumers. For supporting bank operations many banks using core (CORE- centralized online real-time environment) banking service. Basically it means that all branches access applications from centralized data centers. Core banking provides 365/24/7 support to their customers.
In core banking services India, GIS technology is useful to customers as well as employees of bank. GIS model useful in safe monetary transaction route analysis, customers record mapping, debtor record analysis, ATM network solutions, market analysis, bank merger evaluations, client asset mapping, analyzing business continuities etc. Monetary, statistical and operation of bank data can possible to represent spatially by using GIS techniques. It is useful in banking business also.
Banks need to implement customer centric business model. Financial product and services is important functions of banks. Nowadays Market analysis is required feature for banking industry. Banks managing all over world’s consumer information, so database management for bank data and customer relation management is key functions of the bank and that can easily achieved by GIS. Bank database with Location information significant in many ways. Geographic modeling with future plans provides crucial benefits to banking industry.
Why GIS is required in core banking:
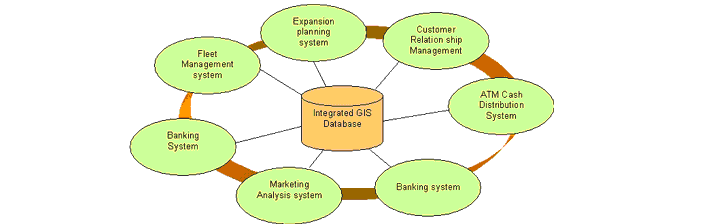
GIS techniques having unique capability to achieve different business goals of the banks. It is important in banks operations, processes and customer management.
- Customer database management
- Improve services using GIS
- Fulfillment of customer needs, ultimately increased user satisfaction
- Business expansion
- Increasing profit rate.
Strategic decision making, effective resource management and operations management can possible by adopting GIS techniques in banking sector.
Market Analysis:
- Essential in highly competitive Business environment.
- Marketing is customer-orientated operation.
- Help to understand financial needs of market & customer.
- Demand & supply can be pinpoint to geographical locations.
- Geo-demographic study of market.
- Census data and customer data uses for market segmentation.
Customer Management:
- Useful in determination of customer characteristics (classification and market segmentation of residential areas)
- Bank branches can be drawn for the catchment areas.
- Provides information about the potential customers. And it is useful of their power for high end core banking facilities
- Postal address can possible to convert a location reference such as a to its corresponding position on a map
- Customers locational display on map in relation to a bank branch
- Ascertain how many customers live or work within one km of certain branch
Asset Management:
- Bank assets management
- Online tracking of Cash status in ATM
- Cash distribution in ATM’s by using cash Van Fleet management
- Performance monitoring of branches of banks
- Requirement to maintain minimum asset condition.
- Advertisement management
So we can recognized that GIS is important in core banking in following ways:
- Market analysis
- Searching and Management of customers
- Competitor analysis
- Focused marketing
- Business expansion planning
- Home loans
GIS implementation phases in core banking are:
- Input data collection: Collection of spatial and non-spatial data of bank
- Design of database: Mapping of spatial data and linking with non-spatial (attribute) data. And including testing and analysis of the data
- Integration, testing and implementation of data
- Application development: gathering of required data, application development and SRS preparation and provision of different banking solutions.
