Cybersecurity in BFSI – Top Threats & Importance
Cybersecurity has been the major area of concern throughout 2022 and now 2023 is all set to witness a new version of cyber-attacks with advanced technologies. Cybercriminals are ready to exploit the technological trends and hunt away into your security domain.

As we transition to a digital economy, cybersecurity in banks is becoming a serious concern. Leveraging methods and procedures created to safeguard our data are essential for a successful digital revolution. The effectiveness of cybersecurity in banks determines the safety of our Personally Identifiable Information (PII), and by extension, ourselves, whether it is an unintentional breach or a well-planned cyberattack.
Current State of Cybersecurity in Banks
According to the S & P Global study on the share of cyber incidents reported across industries in the past years, financial institutions have topped the list and experienced more than a quarter of such security issues.
To make a comparison, the BFSI sector experienced 26% of these cybersecurity incidents, compared to the Healthcare (11%) Software and Technology Services (7%) and Retail (6%), and Retail (6%).
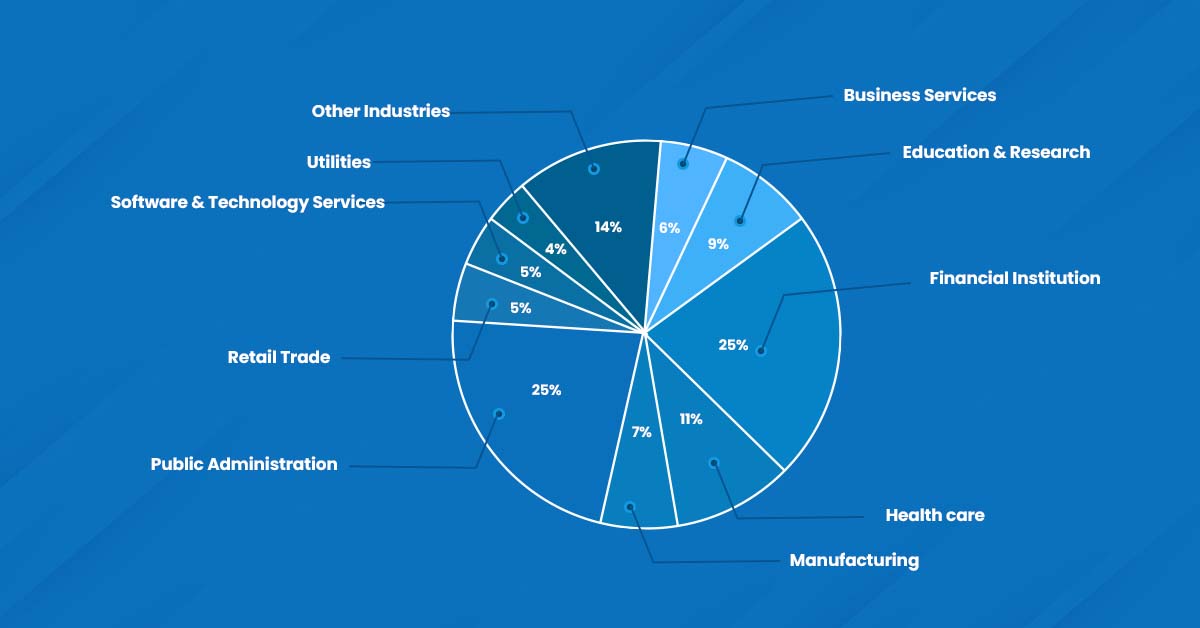
The volume of cyber threats is increasing fast, which shows how critical cybersecurity is to banks today. Particularly for small financial institutions and credit unions that lack the resources to survive, cyber-attacks can be very expensive to endure. Additionally, such financial institutions may suffer catastrophic reputational damage.
Financial institutions are exposed to a wide range of cyber threats that can be managed with effective cybersecurity strategies. In this article, we’ll talk about these threats, how to deal with them, and what resources financial institutions can use to strengthen their cybersecurity procedures. Let’s start.
Common Threats
- Credential Stuffing
Due to the fact that 65% of people reuse the same password across multiple (and occasionally all) accounts, credential-stuffing attacks are one of the most frequent causes of data breaches. As more credentials are revealed as a result of breaches, the opportunity for cybercriminals to use credential stuffing increases; at the moment, the dark web is home to literally billions of compromised credentials.
- Phishing Attacks
The most frequent kind of cyberattack, known as phishing, has changed over the past three decades. They are employed to steal credit card numbers, login information, and other vital user information. By clicking on a malicious link, the system becomes infected with malware.
Phishing attacks are one of the most frequent problems with cybersecurity in banks and can have a devastating impact since they can be used to enter a financial institution’s network and launch a more serious attack like APT (Advanced Persistent Threat).
In an APT, an unauthorized user can access the system and remain undetected for a long time. Significant financial, data and reputational losses may result from this. The Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) recorded 1,025,968 total phishing attacks in the first quarter of 2022.
- Trojans
The idea of the Trojan Horse dates back to the Trojan War. In order to enter Troy, the Greeks deceived the Trojans by riding a horse that was loaded with soldiers.
A Banker Trojan impersonates a legitimate piece of software up until the point at which it is installed on a computer. The term “Trojan” is now used to describe a variety of malicious tactics used by hackers to access secure information.
However, it is a malicious computer program created to gain access to confidential information processed or stored by online banking systems. This type of program is built with a backdoor, allowing outside parties to gain access to a computer.
- Ransomware
A cyber threat known as ransomware encrypts important data and prevents owners from accessing it unless they pay a hefty fee or ransom. Given that 90% of banking institutions have experienced ransomware in the past year, it poses a serious threat to them.
Ransomware poses a threat to cryptocurrencies in addition to posing a problem for bank cybersecurity. Due to their decentralized nature, cryptocurrencies give cybercriminals a chance to hack into trading platforms and steal money.
Sneak Peek
In a first-of-its-kind report, the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) stated that during the first half of the country’s business year (H1) in 2022, ransomware incidents have increased by 51%. Djvu is a “high-risk” virus that primarily targets citizens, and CERT-In blamed it for the increase in attacks in India. The agency also attributed some of the increase to Phobos, a ransomware that “strikes smaller companies and individuals that have less capacity to pay relative to larger businesses”.
- Spoofing
Hackers use a clone site in this kind of cyber-attack. They pretend to be a banking website by –
A. registering a domain with minor spelling modifications or domain extension
B. creating a layout that is identical to the original in both appearance and functionality
The user is given access to the cloned website through a third-party communication platform, such as a text message or email. Hackers steal login information when an unaware user enters it. Much of this situation can be resolved with seamless multi-factor authentication.
Food for Thought
Over the years, cloud services have proven to be very dependable and useful for the banking and financial industries. Banks have benefited from reduced IT costs, a distinctive boost in system uptime, and easy data management.
However, poor planning and execution could negate the advantages that the cloud offers. Therefore, financial institutions must choose the appropriate technological solution to avoid potential security issues.
Cybersecurity in Banks: Ready and Resilient

Banks and other financial institutions are well aware of the weight of responsibility placed on them and the level of risk that they are exposed to when it comes to cybersecurity threats. And so, banks have adapted quickly to the evolving requirements of remote working.
Among the steps taken to increase bank cybersecurity are:
- Addressing knowledge gaps and promoting digital hygiene among staff.
- Ensuring regular software updates and security for employees.
- Changing security procedures, such as launching frequent, tailored awareness campaigns, leads to an increase in staff click rates during recurring anti-phishing tests.
- The limitation of USB device usage.
- Adopting cloud-based contact centers and adopting secure remote hardware.
- Adopting customer-focused security measures, such as extending biometrics and device-based authentication for sensitive transactions over new digital channels.
- Investing money into sophisticated, AI-powered security and fraud detection tools to stop fraud.
- Ramping up cybersecurity spending to fortify new arrangements.
Improving Cybersecurity in Banks – The Way Forward
IT infrastructure of the BFSI sector needs to be strengthened using top-notch security measures and human intelligence to negate cyberattacks. Cyberattacks on the BFSI sector occurring globally can be significantly decreased by utilizing multiple security layers and implementing techniques like multifactor authentication, image authentication, server hardening, biometrics, or implementing Blockchain technology.
With our security products and services at ESDS, you can always rest assured that your business is outfitted with necessary tools and is always protected from cyber threats and that your regular business operations do not interfere.
- 6 Ways AI Reinvents the Security Landscape - January 9, 2024
- Top 6 Current Cybersecurity Trends For 2024 - January 9, 2024
- What Have We Learned from The Recent Cybersecurity Incidents? - January 3, 2024
