Data Protection: The Base Backup In Windows Server 2008 R2

Data protection has always been the most important task for professionals dealing with Windows. Many experts take backups to tape or disk. Larger IT organizations can afford to use more complex solutions offered by other companies. For the rest of us, it is free solutions offered by Microsoft.
Experts formerly used Microsoft’s free utility called NTBackup. But no longer. Windows Server 2008 offers a new set of tools to backup and try to show how easy it is to use them in the new Windows Server 2008 R2. Even if you use the tools to backup offered by other companies, we know the tools and support to be able to quickly create a backup. Please note that this tool does not support backups created with NTBackup.
Installation – Important Information
First, install the backup feature, because it is not installed by default. To do this using the Add Features Wizard in the Server Manager, add the position of program features backup of Windows Server (Figure 1). I will use the command-line tools to be able to use Windows PowerShell, which I describe further below. In order to install these features, you can also use command-line tools such as a ServerManagercmd.exe: C: \ servermanagercmd-install backup-features.
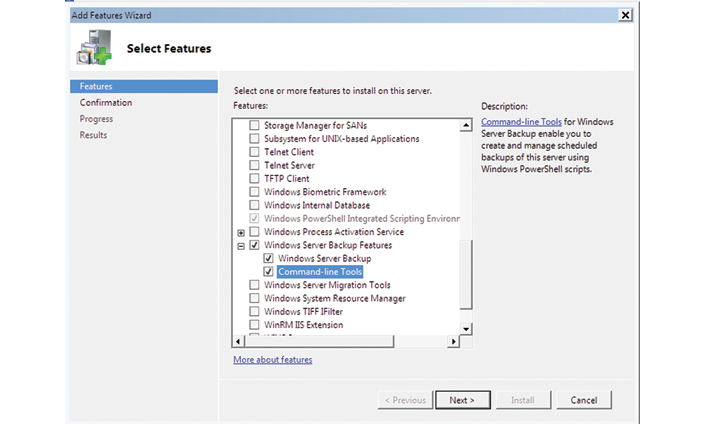
Figure 1 Using the Add Features Wizard to add the position: The program features backup of Windows Server and Tools Command Prompt.
Then, specify backup locations. Backups can be stored on a network, shared in the local volume or on a dedicated disk. You cannot back up data to tape, but due to the increased capacity and wide availability of inexpensive mass storage USB is not a problem. However, there are several aspects.
In the case of a program called Windows Backup, there is considerable redundancy in the context of indexes, directories, and file handling. It looks completely different than the file creation. Zip. We cannot assume that a 100 KB file will be equal to 100 KB of backup, because it will be using much more space.
During the backup to a network share, we need to be careful in terms of accessing control at the file level, and ensure the integrity and security of backups. Also, remember that the execution of the next backup to a network share will replace the previous backup. So best bet is to create subfolders for subsequent backups. A similar situation occurs if backup local volume.
The main advantage when using a network share or volume is that a program called Windows Backup creates a .Vhd that includes all the files in the backup. After determining the location of the backup program for Windows Backup, it creates a top level folder named WindowsImageBackup. This folder contains a backup folder on each computer. Backup versions are arranged by date and you can see folders such as: Backup 2011-02-28 141606th Inside the folder, there are backups of files and file. Vhd. File. Vhd can be installed on Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2. Depending on the requirements of backup and archiving, you can just move this file to ensure long-term storage device, or burn it to DVD.
The easiest and quickest way is to use the included dedicated disk. You can connect the drive internally or externally via USB or FireWire. Microsoft recommends that you provide sufficient space to perform backup 2.5 currently protected data. The disk is formatted and will not be visible under normal management tools, although you can view it in Disk Management. You can use the drives with a maximum capacity of 2 TB.
Backup Job
Backup of Windows is used to create a system for securing the server. It allows for the inclusion of a scheduled backup job to create files and system state or system recovery in terms of “from scratch”. Microsoft is based on the assumption that the user for this purpose will use the one scheduled job. I assume that you are using a feature called Windows Backup due to limited budget and are aware of the limitations in the context of the maximum level of protection.
After installing the Backup of Windows Server Manager, expand Storage and select Backup of Windows Server. In the Actions pane, select “Schedule Backup” which will run the Wizard to schedule backups. On the Introduction screen, click Next.
In step 2 specify the type of backup. You should try to perform a full backup servers.
You can also create custom backup and select items, such as certain files and system state. Later I will present how to perform fast backup file, but now assume that the user wants to fully secure his dedicated server.
The third step is to determine when to run the backup job. Typically, a single backup copy should be sufficient, but the backup job can be run more frequently than once in a day. In the case of critical files, it is recommended to make a few copies per day.
The fourth step is to determine the backup storage location. Microsoft recommends that you use a dedicated hard drive. Please note that this drive will be reformatted and it cannot be used for any other purpose. Backups can also be stored on a network share or volume.
Do not ignore any warnings or restrictions. You might see a warning message reminding you that the drive is formatted.
If not all drives are visible, click Show all available drives to refresh the view. After selecting the new drive, you will see a warning. Then you can confirm your backup settings. In case of errors, click Back and correct the settings. If all the operations are performed correctly, the summary is displayed on the screen. The next day, you can check the node Windows Backup Server in order to familiarize yourself with the results or errors.
Using Windows Backup, you can also perform a one-time backup. In the Actions pane, click One-time backup. You can use the same settings as in the case of a scheduled task, or select other. In other settings, you must run the wizard again and enter the new parameters. For example, you can copy files to a network share. Please note that all backups existing in one folder will be overwritten. The backup begins immediately. If you frequently perform a separate backup job, use a solution based on a script or command-line feature in Windows PowerShell. I will describe this procedure later.
Restoring Data
The version information in the Windows backup timestamp is used. Selecting a Recovery task invokes a simple wizard. Select the appropriate source of backup. The Recovery Wizard displays a control that contains the date and time for all available backup (see Figure 2). Please choose a backup copy. Depending on the type of backup only one option can be available.
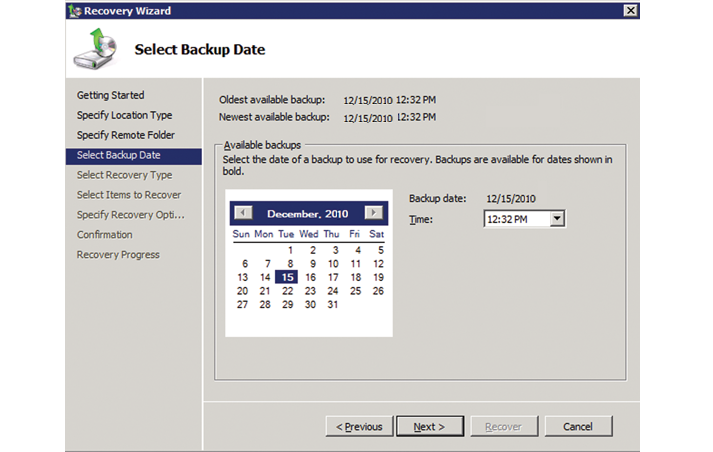
Figure 2 Selection of backups available in the Recovery Wizard.
Then select the type of data to be recovered. Selecting files and folders allows to distinguish the files that will be recovered. Unfortunately you cannot select files from multiple directories. You can easily recover all your files or selected files from one directory. It should be borne in mind when configuring the backup job.
When recovering files, you must specify the destination folder, which may be the original folder or another location. If there is a current version, you can also control the operation after restoring the current file. You can create a copy, so you have the two versions and can replace the existing version, or you can skip the detection of restoring the existing version. The recovery process is carried out immediately.
Using the WBADMIN.EXE tools
If the backup tool is installed from the command line, there are several additional options. When you open a command prompt, it should be familiar with the tool WBADMIN.EXE. With this tool, you can configure a scheduled backup, but using a graphical user interface is much easier. This tool allows you to create convenient backups. After entering the following command displays help on the syntax:
C: \> wbadmin start backup /?
For lack of space I can not describe all the options, but I’ll show you how to use command-line tool, you can periodically make a backup of files to a network share:
@ Echo off:: Demo-Backup.bat: demonstration using WBADMIN.EXE script on a Windows Server 2008 R2 Server backup rem set the UNC share backupshare = \ mycompany-dc01 \ backup files and folders rem include the set include = c: \ scripts c: \ files rem define variables for date time building the folder name set m =% date: ~ 4,2% set d =% date: ~ 7,2% set y =% date: ~ 10,4% set h =% time: ~ 0,2% set min =% time: ~ 3,2% set sec =% time: ~ 6,2% rem Defining a new folder like \ \ mycompany-dc01 \ backup \ RESEARCHDC \ 12152009_132532 set newfolder backupshare% =% \% computername% \% m%% d%% _% s% h%% min%% sec% echo Creating% newfolder% mkdir% newfolder% rem Run the backup echo Backing up%% include the %% wbadmin newfolder start backup-backuptarget:% newfolder% include:% include%-quiet rem Clear variables Set backupshare = set include = set m = d = the set set y = h = set set set min = sec = set newfolder =
If you do not want to replace all existing backups, so I create a new folder, named in part consisting of a computer name and the date and time stamp. With the code contained in a batch execution of that sentence is not difficult. The main function of the script is called WBADMIN.EXE tool to create a backup copy in a particular share. To customize this step, please refer to the help on the syntax. With the script itself, you can configure a scheduled task in Task Scheduler. The Backup Wizard allows you to create only one scheduled task, but with WBADMIN.EXE tool you can create any number of tasks. In addition, this tool also allows you to backup system states.
To view the tasks performed for the backup, use this command: C: \> get wbadmin versions.
Pay special attention to the version identifier, because this value will be necessary to recover the files using the command WBADMIN (in this order, you can also use the Recovery Wizard.)
Backup using Windows PowerShell
Backup using the command line, you can also create applets with PowerShell commands in Windows Backup. To gain access to these additives, you must first load the Backup snap-in Windows:
PS C: \> add-pssnapin Windows.ServerBackup
To view the applets included the command, use the Get-Command:
PS C: \> get-command-pssnapin windows.serverbackup
Unfortunately the backup job is a multistep process. Commands can be entered at the command interactively, but it is easier to do this using a script. Below is a version of the original batch file format version of Windows PowerShell:
# Requires-version 2.0 # requires-pssnapin Windows.ServerBackup # Demo-WBBackup.ps1 $ policy = New-WBPolicy $ files = new-WBFileSpec c: \ scripts c: \ files Add-wbFileSpec-policy policy-$ $ files filespec $ backdir = ("\ \ mycompany-dc01 \ backup \ {0} \ {1: MMddyyyy_hhmmss}"-f $ env: computername (get-date)) write-host "Creating $ backdir"-foregroundcolor Green mkdir $ backdir | out-null $ backupLocation = New-WBBackupTarget-network $ backdir Add-WBBackupTarget-Policy $ policy-Target $ backupLocation write-host "Backing up files is the $ $ backdir"-policy $ foregroundcolor Green Start-WBBackup-Policy $ policy
Applets Windows PowerShell commands are for creating rules for the performance.
This shall include files or volumes used to back up or delete it, and also allows you to perform backups of files and set other options. Moreover, it is possible to create recovery tasks such as: “the state system” and “from scratch”. In this example, a straight back up of several directories will be performed. Applet Start-WBBackup start backup job.
In the command applets Backup utility of Windows, unfortunately, it is missing one vital element: an applet which allows to restore data. I suspect that the creators did not want to provide tools that automate tasks, but for this purpose you can use WBADMIN.EXE. Perhaps this cmdlet will be added in future releases. Currently, files can be recovered using the Recovery Wizard or the tool WBADMIN.EXE.
Now, on the user
Once you get acquainted with these tools, you will probably notice that the world does not end with the Backup program in Windows. It should also reflect on their usefulness in specific strategies for backing up and using them in future business plans. In several respects Backup Windows is limited, however, to scripts and application files.
Vhd provides some opportunities to circumvent these restrictions. The user simply needs a little more consideration of the execution of specific tasks. And as with all softwares, to make backups before serious use of them in the organization to carry out several attempts to “dry.” We cannot allow a situation when the user knows the tool only when problems arise.
Explore the tools on the horizon when a storm is not coming, not at the time of the disaster.
- How Cloud Computing Is Changing The Labor Market - March 25, 2015
- Adopting Infrastructure as a Service Can be a Good Deal - March 17, 2015
- Will Virtualize? Take These Six Points Into Consideration - March 12, 2015