Database management System– Your guide to managing the data lifecycle
Using database management, a human can organize, store, and retrieve data from a computer. Database management is another term for a database administrator’s (DBA) procedures for data storage, operations, and security throughout the data life cycle.
Database administration is not a single thing; instead, it refers to a set of procedures (and, for some, a specific technology) that regulate the lifespan of business data. Businesses have discovered that database management is essential for controlling this influx of data as it rises in order to prevent subpar application performance and lessen any impact on compliance and continuity.

A company can use a variety of “database management” strategies and practices to lessen or avoid the negative effects of exponential, unchecked data expansion.
What is a Database Management System mean?
A database management system is a software-defined system that effectively manages databases, as opposed to database administration, which refers to a set of best practices. Database management programs like FileMaker Pro and Microsoft Access are widely used. Users in this system have access to databases’ contents and can read, update, add, and delete data as necessary. When used as an interface, a database management system gives end users access to their databases and gives them the right tools they need to organize and access the data as needed.
The engine that enables users to access the data within a database, as well as the database schema—the database’s organizational structure—, are all managed by a database management system. A database management system provides security and guarantees data integrity, but some systems are also used to automate rollbacks, restart databases, log activity, and conduct audits.
How Does Database Management Work?
Simply put, a database manager and their team are in charge of assuring the functionality and health of a company’s databases. The above-mentioned best practices guarantee that organizational databases function as they should. However, using a database management system (DBMS) gives you the control and insight you require.
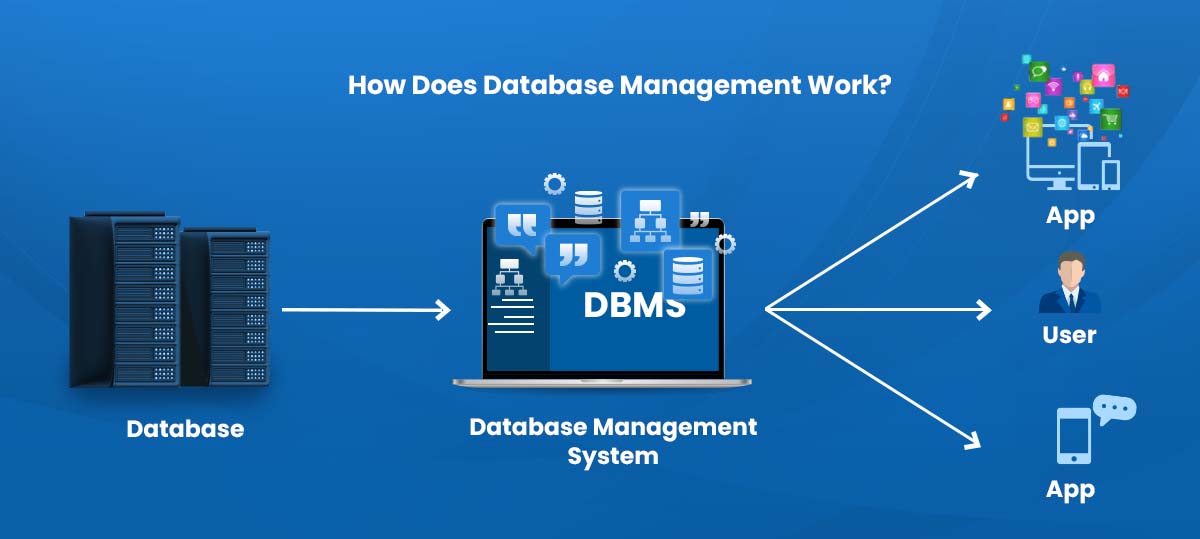
A database management system basically functions as follows: Your database files are organized, and it gives users easier access to and controls over their data. In order to achieve this, a DBMS gives users the ability to modify, create, and update data as needed in their database files. A DBMS can then save and retrieve the data from the database from there.
A DBMS provides five main functions:
- Allowing numerous people to view a single database at once.
- Establishing and maintaining user access permissions and security guidelines.
- Frequent data backups and speedy data recovery in the event of a breach.
- Establishing database policies and guidelines to safeguard data integrity.
- Supplying “dictionary” definitions and summaries of the information at hand.
Why do Businesses Need Database Management?
There are no indications that the amount of data will decrease. For the following reasons, businesses are spending money on database administration chores, database managers, and database management systems:

- Keep the business going as intended.
- Keep an eye on your clients, your data, and your staff.
- maintain the performance of the database and applications
- Organize and save various unusual forms of data.
- Automate database operations and tasks
Particularly, given the growing volume of data that both humans and machines produce every day, the advantages of a database management system are difficult to overlook. Enhancing the security of data kept in databases is one of the more prominent advantages. Businesses can improve end-user access to data and facilitate data sharing across the enterprise by using DBMS. Because they have access to the precise data they require, these end users can produce faster sales and make decisions.
Additionally, organizations may get rid of the issues caused by data inconsistency, which comes when the same data is present in separate places in varied forms. A DBMS gives businesses a thorough understanding of how data is shared, preventing needless duplication of data. A DBMS also enables businesses to enforce data security and privacy guidelines to lower the chance of a data leak.
In the end, the data supplied will enable end users to make wise judgments. Better, more reliable data translates into high-quality, actionable information that can support users’ decision-making with the precise data they require. In the end, this boosts productivity across the board for the company.
Advantages of DBMS
Controls database redundancy: Because it keeps all the data in a single database file and stores the recorded data in the database, it is able to control data redundancy.
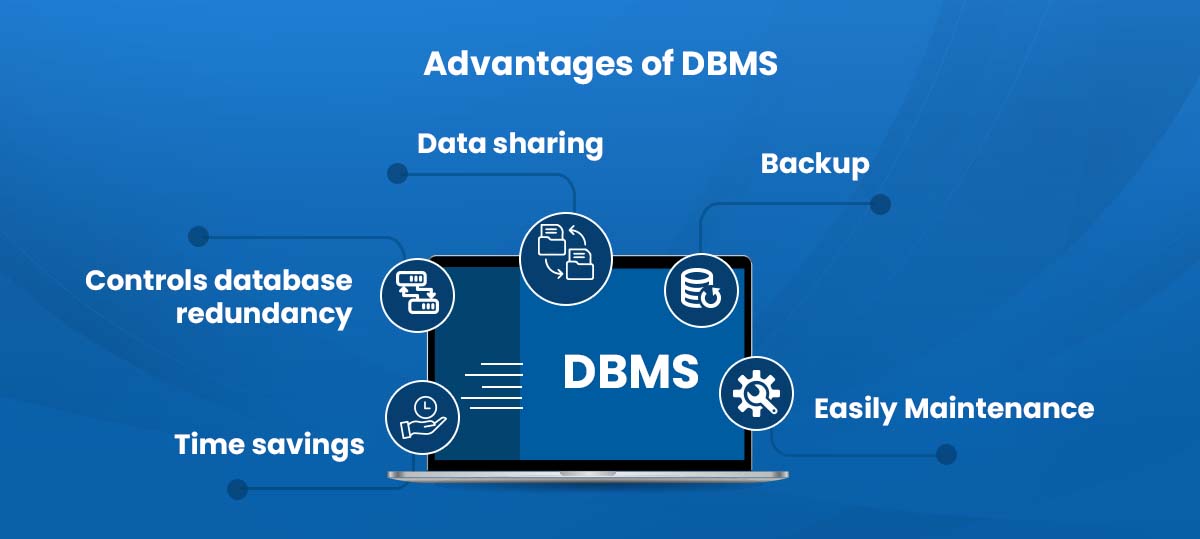
Data sharing: A DBMS enables an organization’s authorized users to distribute data among several users.
Easily Maintenance: Because the database system is centralized, it may be simple to maintain.
Time savings: It lessens the requirement for maintenance and development time.
Backup: It has subsystems for backup and recovery that automatically back up data in the event of hardware or software problems and restore the data as needed.’
How to Choose a Database Management System?
The optimal DBMS for your organization will depend on a number of variables and priorities, depending on whether it wants to implement database management best practices or not.
The first and most important step in choosing the best DBMS is understanding your current database(s). Because each database will have a unique set of information, organizations should be aware of their requirements. A quality DBMS will provide a consolidated view of your data’s status, allowing you to understand where it is being stored and how it is being used. A DBMS will also provide access to data across numerous applications without the need for data replication.
Additionally, firms should consider if they can sustain the additional memory and CPU requirements that a DBMS, like many systems, will entail. The advantages of DBMS, however, are real, particularly when it comes to sensitive data that is constantly developing, like that seen in healthcare organizations.
Our verdict
DBMS offers a variety of user interfaces, including graphical user interfaces and application program interfaces. Database management systems are continually changing, despite the fact that they are an established technology. The global DBMS market had a value of around $63 billion in 2020, and Expert Market Research estimates that it will increase by 12.4% between 2022 and 2027. Companies may invest in the best DBMS solutions provided by ESDS and optimize the power of data available to their organization by understanding the ins and outs of this technology.
- Why does your business need Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)? - May 15, 2024
- Are your business endpoints completely secure? - March 26, 2024
- Is Colocation key to transforming your data center management strategy? - March 22, 2024
