Software-Defined Storage: The Storage Brain of the Cloud
What is Software-Defined Storage?
A lot has been said about Software-Defined Storage (SDS) and what it is. Every vendor utters his their own definition of SDS for product PR and marketing purpose. Here is the actual unbiased definition divided in a few simple-to-fathom parts:
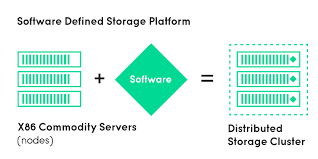
SDS is the process of utilizing the community industry standard hardware (servers & disks) and intelligent software-based techniques to give storage functionality like create, deploy, manage and monitoring storage resources and infrastructure.
- It enables abstracting or separating storage services from hardware devices by using software or programmatic access to extract and manipulate storage resources.
- SDS assumes that the hardware underneath—regardless of that hardware’s cost or age—will eventually fail, and so it plans for that failure by distributing workloads across the infrastructure.
- It’s an approach to data storage wherein software provisions and manages storage independent from underlying hardware.
Who uses Software-Defined Storage and why?
Traditional propriety hardware:
By helping one get rid from propriety vendor hardware storages and dependency, SDS allows for use of community X86 based storage hardware. It is also usually easier to make quick changes to SDS configurations than it is on storage running on dedicated hardware.
Reduce storage OpEx and CapEx, basically the entire IT stack:
SDS will enable them to have more flexibility in their procurement model and significantly lower storage costs. SDS is typically more agile and cost-effective than traditional NAS and SAN approaches to storage. It also reduces downtime, adds features and unifies storage from over 400 storage systems to make block storage more efficient, agile and cloud-ready.
Simplify:
SDS helps simplify things all the way from buying hardware and installation through migration, support and ongoing maintenance to upgrades of the storage system.
Technology:
It is a better technology in terms of scalability, flexibility, performance, reliability and business agility.
Securely grow:
Organizations can incrementally add capacity a few nodes at a time so that as demand increases, storage can grow to meet the demand — as opposed to having to invest in more and more hardware for traditional storage arrays. It can manage data growth from under 100TB to many petabytes with ease. You gain leading data integrity and security and native hybrid cloud options.
Exceed expectations:
SDS optimizes big data analytics and clustered applications with high-performance, scalable storage that enables global collaboration, simplifies workflows and lowers costs with cloud tiering.
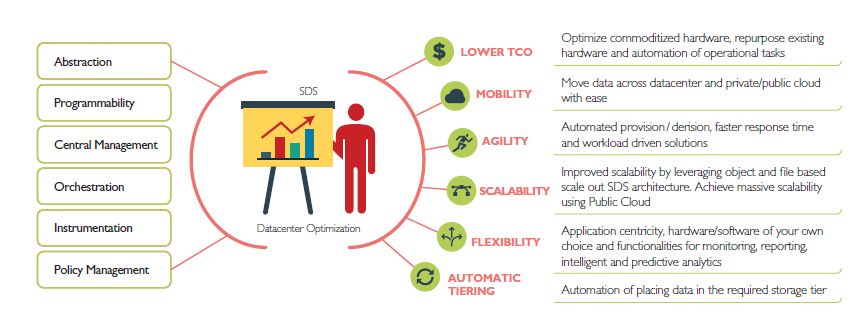
Key Attributes of Software-Defined Storage
SDS transforms existing heterogeneous physical storage into a simple, extensible, and open virtual storage platform. The key features of SDS are as follows:
Scalability:
Equipped with elastic scale-out and in-place analytics, SDS has seamless ability to scale the storage infrastructure without disruption to the specified availability or performance.
Reliability & Flexibility:
SDS optimizes IT agility and delivers continuous value. Besides being truly stable and always available this storage option lends more infrastructure and application flexibility as well.
Performance:
SDS systems deliver extreme performance and capacity with enterprise grade protection. They help build better clouds and develop modern apps at 65% cheaper than Public Cloud. They can also analyze more data than other systems.
Transparency:
The SDS protocol is extremely transparent providing an innate ability for storage consumers to monitor and manage their own storage consumption against available resources and costs.
Intelligent Storage Optimization:
SDS multi-tier architecture and control helps to push information to a specific type of repository. One can control performance and capacity pools and further deliver information to the appropriate storage-type.
All (Block/File/Object) storage together:
SDS does support Block, File and/or Object interfaces that further support applications written to these interfaces.
Unified management:
SDS has a unified storage management interface that provides an abstract view of the storage infrastructure. Besides automating storage provisioning, capacity management, availability monitoring and reporting, it also reduces the cost of maintaining the storage infrastructure.
Data protection you can trust:
Whether it’s back up, disaster recovery, data governance or solutions for DevOps, SDS data protection meets today’s most difficult business challenges.
Self-service:
Resource pooling enables multi-tenancy, and automated storage provisioning enables self-service access to storage resources. Users select storage services from a self-service catalog and provision themselves.
Open and extensible:
Extensible architecture enables integrating multi-vendor storage, and external management interfaces and applications into the SDS environment through the use of application programming interfaces (APIs).
How does Software-Defined Storage work?
- Software-Defined Storage breaks traditional hardware lifecycle and the traditional storage appliance model.
- With software abstracted from hardware, customers can acquire hardware and software independently.
- Customers can deploy them on the hardware of their choice rather than being locked into a narrow proprietary hardware platform or SDS can be downloaded as software.
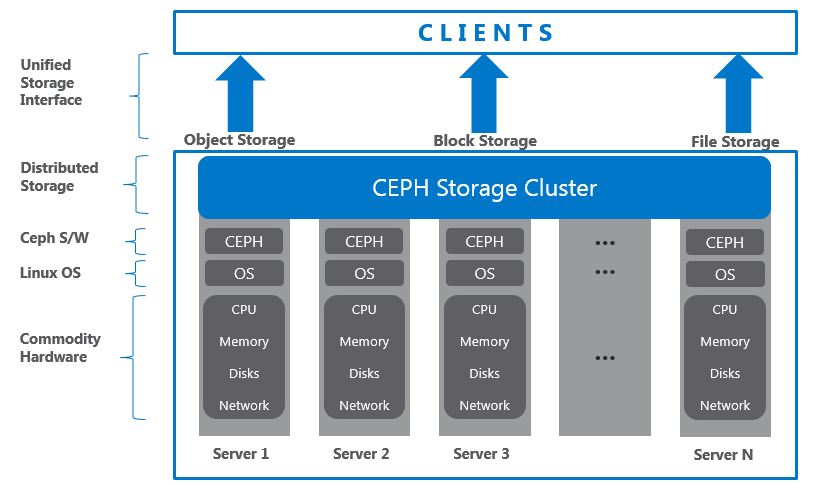
CEPH is very known and grown open source Software-Defined Storage platform and provides highly scalable object-, block- and file-based storage under a unified system. CEPH SDS clusters are designed to run on commodity hardware, using an algorithm called CRUSH (Controlled Replication under Scalable Hashing) to ensure data is evenly distributed across the cluster and that all cluster nodes can retrieve data quickly without any centralized bottlenecks. It replicates and rebalances data within the cluster dynamically—eliminating this tedious task for administrators, while delivering high-performance and infinite scalability.
The Storage Brain of the Cloud
The advent of Software-Defined Storage is changing the storage industry, just as SDN has changed networking. To date, storage has been based on a wide variety of storage software, hardware components, and storage-area networking (SAN) components. Large vendors such as EMC, IBM, and NetApp have built multi-billion-dollar businesses selling specialized storage and SAN components. However, a number of startups have taken advantage of the SDX movement to push more software-based solutions. Startups such as EMC-ScaleIO, MAXTA, hedvig Atlantis Computing, Coho Data, and Nutanix are building software and hardware systems targeted at virtualized Data Centers and SDS environments.
The latest trend in storage and SDS is to build a network of simple, massively scalable hardware arrays – whether they be flash storage, hard drives, or a combinations – and connect them together with a SDS system so that more storage can always be added by adding hardware. This is known in the business as a ‘scale-out’ architecture.
- Software-Defined Storage: The Storage Brain of the Cloud - June 13, 2018
- Proactive Approach: The key to drive success - May 30, 2018