Top methods for Backup and Recovery you Must Know!
The vital purpose of a backup is to ensure protection for critical business data to recover in case of data loss, system failure, or a cyberattack. As a part of any sensible disaster recovery plan, backup has become essential. Sadly, more than 50% of businesses have experienced data loss as a result of not having a proper backup or access to one. Even the biggest brands and companies have faced data loss due to either cyberattacks or human error.

Unfortunately, natural disasters such as fire, earthquake, flood, or even power failures have in the past been the cause of several data loss cases. In this digital transformation era, Data is an invaluable asset for businesses of any type or industry, and losing this precious data can lead to massive damage in more than one way for organizations. According to a report, the average total cost of data breaches in 2022 was about $4.35 million. In fact, India was in the top 45% of cyber-attacks in the year 2022 among other countries. The major brunt of these attacks and targets was the government institutions, resulting in an increase of 95% rise in the year-on-year report for our country.
While backup sounds like a simple process of copying data from one system to another, it has several critical aspects attached to it, such as including application and product data, information of accounts, members, other business records, and employee data among other crucial information that is vital for business operations. Essentially, the backup must be able to help in the regular day-to-day activities without facing any issues internally as well as to the customers. Likewise, recovery ensures utilizing the backup copies in the structure format given, restoring them to their assigned places, and making them back in order to keep the business in continuity. Businesses have realized the importance of having proper backup and recovery plans and have opted for a trusted partner that provides an assured business continuity plan as well.
There are basic industry guidelines and regulations that require various standards for backup and recovery as a process, there are also general practices that companies follow. The 3-2-1 rule, which means storing 3 copies of your data in 2 different storage types, and keeping one of the copies at an off-site location is the safest option.

3 copies of data—which includes original data + two duplicates. That ensures a lost backup or corrupted files do not affect recoverability.
2 different storage types—To reduce the risk of failures if a specific medium does not work out. Internal and external hard drives, removable media, or cloud storage are used generally.
1 copy off-site— Eliminating the risk associated with a single setup. These Offsite duplicates are required during a robust disaster and data backup recovery strategies and failure of local outages.
While following the general industry practices, cloud solutions have been of great help to not only store the data but also back it up regularly and recover swiftly when needed along with the ongoing business operations. Now that we have understood the importance and need for backup and recovery, let’s learn about the different methods of backup and recovery.
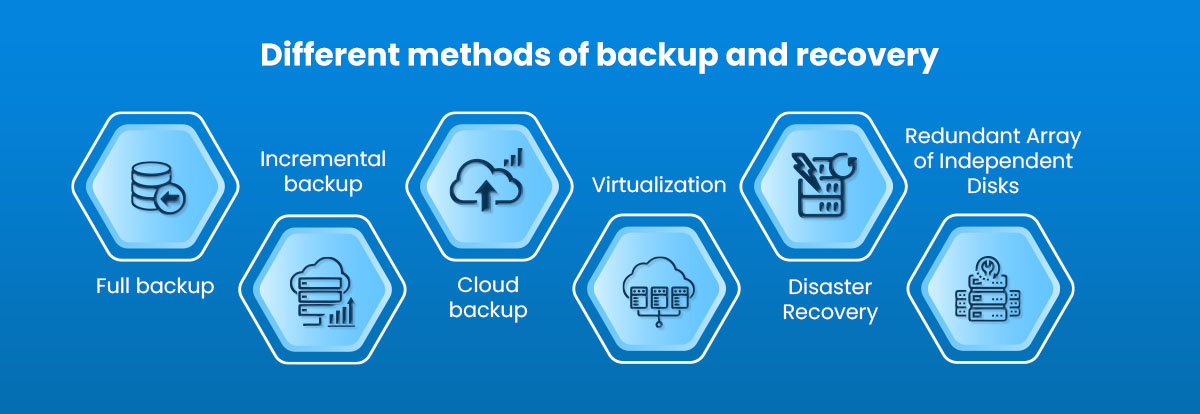
Full backup: This involves copying all the data on a system or device to a backup location, such as an external hard drive, cloud storage, or tape drive. This method is time-consuming and requires a lot of storage space, but it ensures that all your data is backed up.
Incremental backup: Incremental backup involves copying only the data that has changed since the last backup. This method is faster and requires less storage space than a full backup, but it requires multiple backups to restore all the data.
Cloud backup: Cloud backup involves storing your data on remote servers maintained by a cloud service provider. This method provides off-site storage and protects your data against physical disasters and theft.
Virtualization: Virtualization involves creating virtual machines that can be backed up and restored independently of the underlying hardware. This method provides flexibility and simplifies backup and recovery
Disaster Recovery: Disaster recovery involves planning and preparing for the worst-case scenario, such as a natural disaster, cyber-attack, or hardware failure. This method includes creating a disaster recovery plan, testing the plan, and ensuring that the necessary resources and tools are available.
Redundant Array of Independent Disks: RAID involves using multiple hard drives to create a single storage system that offers redundancy and protection against data loss. This method provides high availability and can withstand hardware failures.
As per the business need, the method of data backup can be chosen for action. These backup methods vary in quality and quantity of the data as well. It’s essential to choose a backup and recovery method that provides the right level of protection and meets your budget and time constraints.
Some of the best practices for a full-proof disaster recovery or business continuity include both backup and recovery as 2 sets of approaches. A regular and consistent backup solution and a well-defined recovery plan put together in place can ensure data protection and save you from unplanned data loss. It is only wise to be prepared for the worst-case scenario while being able to run the daily operations uninterrupted. Cloud solutions provide the relief of daily operations along with regular backup and recovery process which is achieved automatically. For businesses seeking an off-site data storage backup cloud becomes a safe option.
- Unlocking Data’s Time Machine: The Importance of Database Point-in-Time Recovery - August 2, 2023
- Future-Proof You’re Data: Navigating the World of Enterprise Backup and Data Protection Solutions - July 7, 2023
- Unleashing the Potential of Long-Term Data Retention: Exploring Trustworthy Backup - May 31, 2023
