What is cloud-based disaster recovery?
Disaster recovery is the process of planning, complying with policies, and applying methods for restoring critical technology infrastructures and systems in the event of disaster. Cloud-based disaster recovery includes cloud resources that duplicate and maintain data, applications, and workloads to help rapidly and effectively restore during disruption.
Traditional disaster recovery mechanisms are costly, including on-premise backup and secondary data centers. Cloud-based DR is much easier to operate and affords additional advantages such as flexibility and cost-effectiveness. It can replicate data in the cloud to places that result in geographic redundancy and faster recovery times.
The benefits of cloud-based disaster recovery
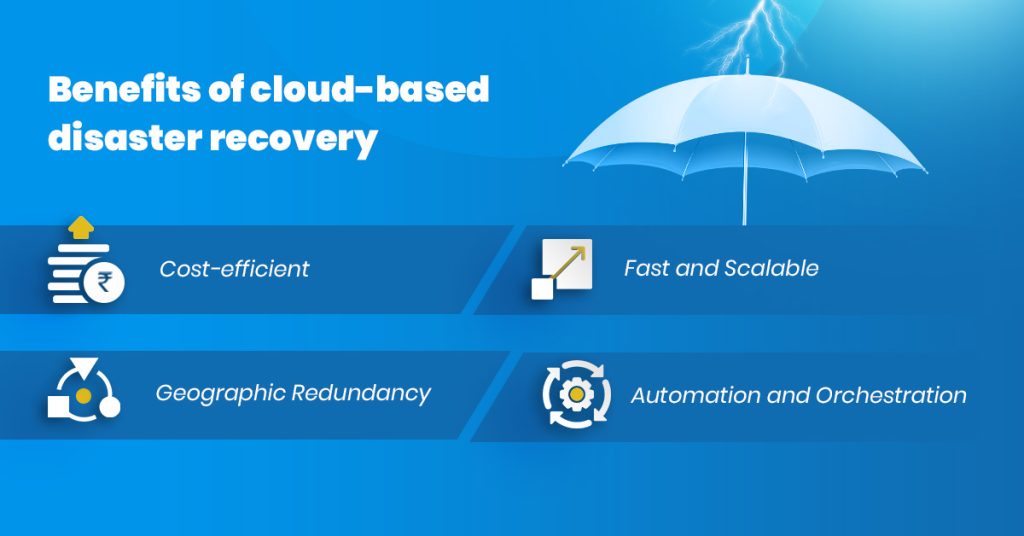
- Cost Efficiency: Traditional DR solutions require colossal hardware, software, and associated maintenance investments. DR in the cloud eliminates concerns about physical environments and, therefore, helps reduce capital expenditure. There is no need to pay for storage or computing resources that are not in use, thereby making the process cost-effective.
- Scalability: The cloud resources are very highly scalable. The DR can be dialed up or down according to the company’s requirements. A growing or scaling down business will find that cloud-based DR adapts to these changes without significant overhauls.
- Speed and Flexibility: Cloud-based DR solutions are far faster than traditional disaster recovery modes. Fast recovery ensures data restoration from the cloud quickly, minimizing business downtime. The flexibility of the cloud provides additional advantages to the DR plans during the testing and update phase.
- Geographic Redundancy: The cloud service provider usually has data centers at different locations. Geographic redundancy ensures that data is replicated across various regions, protecting against local catastrophes and increasing resiliency in general.
- Automation and Orchestration: Most cloud-based DR solutions have automation and orchestration capabilities. Automation features lower the potential risk of human failure and ensure that recovery procedures have been executed effectively and accurately.
Best practices for cloud-based disaster recovery
- Comprehensive DR Planning: A well-defined DR plan is the backbone of any disaster recovery process. Organizations should identify critical systems and data, define recovery goals for them regarding RTOs and RPOs, and describe precisely how they will recover in the steps provided. A DR plan is effective only if it is updated and tested at regular intervals.
- Data Encryption and Security: Like any other DR strategy, data security is the top concern. This refers to encrypting the data both at rest and in transit so that, during replication and recovery, its movement doesn’t compromise the criticality of information. Robust access controls and monitoring are needed to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Regular Testing and Drills: It will further show the shortcomings and what needs to be improved by testing the DR plan using simulation exercises and drills regularly. In doing this, all stakeholders will know their roles and responsibilities during a disaster and that the recovery process may turn out smoothly.
- Choosing the Right Cloud Providers: Choosing a reputable cloud service provider with a robust infrastructure and a top disaster recovery track record is essential. To align your requirements, assess their service level agreements, data center locations, security measures taken, support services, etc.
- Implementation of multi-cloud strategies: Depending on a single cloud provider, the organization is exposed to risks if it falls or experiences some other form of failure. Data and application replication in multiple clouds is a multi-cloud strategy that increases redundancy for even greater resilience in case of failures.
Use cases of disaster recovery
Disaster recovery plans differ according to an enterprise’s size, industry, and priorities. After performing business impact analysis and risk analysis, a company can require different DR plans for various assets like warehouses, data centers, or crucial equipment.
A good DRP essentially ensures quick and secure recovery of business procedures. Here are five business disaster recovery use cases to help you understand the importance of choosing the right solution and creating a solid plan.
Cyber Attacks
Cyber-attacks are destructive and extremely expensive. Many companies turn to disaster recovery (DRaaS) providers as a service to get back on their feet. DRaaS providers host and manage the recovery infrastructure, plan for its responses, and assure quick returns to business operations.
DRaaS providers help restore system access, reduce system downtimes, and restore investor confidence while ensuring compliance in many regulated sectors.
Cloud or local server outages
Many companies have a failover/failback process if there is an outage at the cloud or the local server. If an outage occurs, operations are maintained by switching to a backup environment. Users might not even realize the switch. Operations switch back to the primary server when it returns online, ensuring no data loss and no services are shut down.
Network connectivity failures
Network failures can result in financial losses associated with expensive downtime and negative publicity. Network recovery plans enable organizations to respond to losses in Internet access, cellular communications, local area networks, and wide area networks.
Network recovery plans should document procedures and responsibilities. As in the case of cyberattack DRPs, network failure DRPs are typically outsourced to the particular DRaaS providers.
Datacenter crashes
These could be numerous, like power outages, human error, or compliance-related problems. DRPs for datacenters concentrate on two major things: the facility’s security and the capability to return to work after an event.
These strategies measure risks and research the main parameters of the physical environment, connectivity, sources of power, and many more. The scope is usually broader in DRPs for a data center, as many threats exist.
The future of cloud-based disaster recovery
The face of disaster recovery will continue to evolve with technology. New trends, especially AI and ML, promise to elevate cloud-based DR solutions. AI-driven analytics can detect potential failures and thus trigger recovery before an outage occurs, reducing downtime and improving resilience.
On the other hand, integrating edge computing with cloud DR would further enhance recovery capabilities by reducing latency through processing data closer to the source for faster recovery. This is essential for applications requiring minimum downtime, such as healthcare or manufacturing.
Conclusion
In this modern age, an organization’s backbone is its critical data, which must be protected. Cloud-based disaster recovery delivers robust, scaled, and cost-effective solutions to defend against digital downpours. With the power of the cloud, better recovery times, security, and resilience could be built into the face of disasters.
With downward auto-scaling technology available on the cloud, ESDS offers a highly affordable offsite warm disaster recovery solution compared to traditional cold backup solutions. This ensures that all virtual machines are kept in miniature mode until needed for a disaster recovery drill or even in the event of a primary site failure.
Implementing best practices, regular DR plan testing, and keeping up with new technologies will prepare a business for whatever may happen. Similarly, as the digital world continues to change, so will the umbrella of cloud-based disaster recovery, continuing to protect organizations from the storms that hit the digital world.




